
Case-hardening process that introduces nitrogen into the surface of a solid ferrous alloy by holding the metal at a suitable temperature (below Ac1, for ferritic steels) in contact with a nitrogenous gas, usually ammonia. Does not require quenching for production of a hard case.

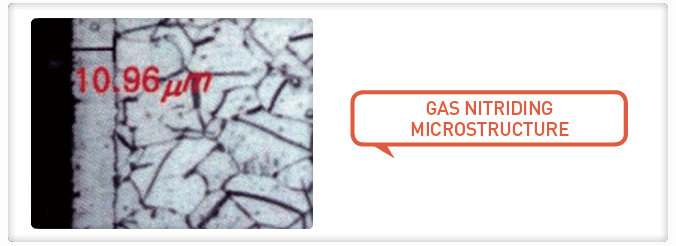
EXPECTED PROPERTY
- + Less distortion and deformation
- + White layer gives corrosion, wear and fatigue resistance
- + Better fatigue strength
- + Remain inner toughness
- + Workable with low carbon steel
Application
- + Automotive (plates, gears, parts etc.)
- + Die Casting / Plastic injection molds
- + Ship & aircraft parts
- + Industrial, electric parts
- + Hot forging molds

- Traditional case-hardening process in which carbon is dissolved in the surface layer of a low-carbon steel at a temperature sufficient to render the steel austenitic, followed by quenching and tempering to form martensitic microstructure.
- Carbonitriding hardens surface of steel by diffusing carbon and nitrogen simultaneously into steel in carburizing atmosphere with ammonia gas at around 850`c, lower than typical carburizing temperature.
- It offers several advantages over carburizing, including low distortion, greater resistance to softening during tempering and fatigue strength.

Operational property
- + Selective hardening
- + Maintain inner toughness & wear, fatigue enhancement where high frequency heated
- + Stable carburized depth
- + Less oxidation & decarbonizing
- + Less deformation, less size scattering
Application
- + Deform sensetive Automotive parts
- + Industrial parts
- + Vessel & aircraft parts

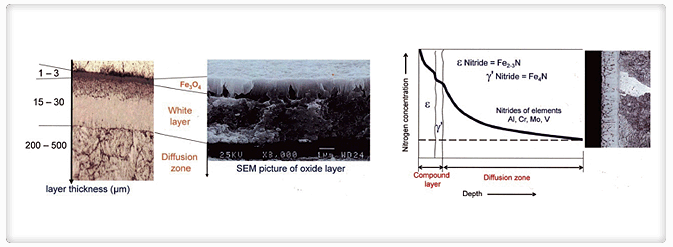
- Oxynitriding forms Fe3O4 at the outer layer over compound layer

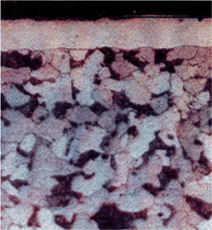
EXPECTED PROPERTY
- + Wear ,fatigue resistance
- + Fe3O4 gives better corrosion resistance
- + Product color(Black & Blue)
- + Alternative for hard Cr plating
- + Workable with low carbon steel
APPLICATION
- + Automotive (plates, gears, parts etc.)
- + Die Casting / Plastic injection molds
- + Industrial, electric parts
- + Mold & Dies

- Ion nitriding extends conventional nitriding processes using plasma discharge physics. In a vacuum, high-voltage electrical energy is used to form a plasma through which nitrogen ions are accelerated to impinge on the work piece. Ion bombardment heats the product, cleans the surface and provides active nitrogen.
Plasma Nitroxidation

Operational property
- + Precise control on diffusion layer
- + Precise temp control offers deformation stability
- + Heat treating stainless
Application
- + Automotive (plates, gears, parts etc.)
- + Die Casting / Plastic injection molds
- + Industrial, electric parts
- + Mold & Dies
Feature
- + Continuous Nitriding & Oxidation in same process
- + Oxidation with No change in surface roughness
- + Enhanced lubrication characteristic
- + Corrosion, fatigue resistance


























![Plot No. 126, Samathuvapuram, Mappedu, Ulundai[Post] Thiruvallr [TK && Dist] Tamilnadu, India Tel. +91-44-2769-9814 COPYRIGHTⓒ 2013 DONGWOO SURFACETECH(INDIA) Pvt.Ltd. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.](../images/common/copyright.gif)